 Protocol for the PreSERVE-AMI trial, one of the largest studies of bone marrow cell therapy for heart attack in the United States. Researchers made real progress in determining the cell type and dose that can benefit patients.Emory UniversityIn this study, doctors treated heart attack patients with their own bone marrow cells, selected for their healing potential and then reinjected into the heart, in an effort to improve the heart’s recovery. In the PreSERVE-AMI phase II trial, physicians from 60 sites (full author list) treated 161 patients, making the study one of the largest to assess cell therapy for heart attacks in the United States. The study was sponsored by NeoStem, Inc.
Protocol for the PreSERVE-AMI trial, one of the largest studies of bone marrow cell therapy for heart attack in the United States. Researchers made real progress in determining the cell type and dose that can benefit patients.Emory UniversityIn this study, doctors treated heart attack patients with their own bone marrow cells, selected for their healing potential and then reinjected into the heart, in an effort to improve the heart’s recovery. In the PreSERVE-AMI phase II trial, physicians from 60 sites (full author list) treated 161 patients, making the study one of the largest to assess cell therapy for heart attacks in the United States. The study was sponsored by NeoStem, Inc.
"This was an enormous undertaking, one that broke new ground in terms of assessing cell therapy rigorously," says the study’s principal investigator, Arshed Quyyumi, MD, professor of medicine at Emory University School of Medicine and co-director of the Emory Clinical Cardiovascular Research Institute. "We made some real progress in determining the cell type and doses that can benefit patients, in a group for whom the risks of progression to heart failure are high."
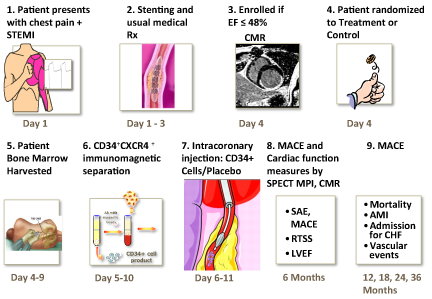
All participating patients received the standard of care -- stent placement -- and were only enrolled if, four days after heart attack and stenting, their ejection fraction (a measure of the heart’s pumping capacity) was less than 48 percent. The average starting ejection fraction was 34 percent, a sign of severe injury to the heart. After enrollment, patients had cells extracted from their bone marrow and received an intracoronary injection of sorted bone marrow cells or a placebo. Not all patients received the same dose of cells. Patients were supposed to receive a minimum of 10 million cells but some received more, up to 40 million.
Several previous studies of cell therapy for heart attack have used unsorted bone marrow cells. Bone marrow contains rare cells called endothelial progenitor cells, which are thought to promote healing and recovery of blood flow. In this study, extracted bone marrow cells were shipped to NeoStem’s facility and a marker for endothelial progenitor cells called CD34 was used to select progenitor cells before cells were returned for intracoronary injection.
Recovery and outcomes were assessed in several ways: MACE (major adverse cardiac events, ranging from hospitalization for chest pain to death), ejection fraction, measured by magnetic resonance imaging, and perfusion or blood flow in the heart, measured by SPECT imaging. Cardiac imaging was performed six months after treatment, and MACE came from an average of twelve months of follow-up.
MACE occurred in 14 percent of control patients (n = 83), in 17 percent of those of who received less than 14 million cells (n = 47), in 10 percent of those who received greater than 14 million cells (n = 31; this includes the next group), and in 7 percent of those who received greater than 20 million cells (n = 15). Mortality was 3.6 percent in the control group, and zero in the entire treatment group.
Displaying a similar dose-dependent trend, starting from an average of 34 percent, ejection fraction increased 4.9 percent in controls, 3.1 percent in the group receiving less than 14 million cells, 5.8 percent in the group receiving more than 14 million cells, and 10.2 percent in the group receiving more than 20 million cells. There were no significant effects on improvement in blood flow in the heart, as measured by SPECT imaging.
The patients who received treatment had delays in getting stents (average 931 vs. 569 minutes), which puts the treated group at a disadvantage in terms of the heart’s recovery. This was a chance effect resulting from randomization to placebo vs. treatment and not inherent to the treatment process, since all bone marrow-related treatment procedures occurred after stenting.
According to Quyyumi, FDA officials have told cell therapy investigators that MACE (clinical outcomes) are the important measure of success and SPECT imaging is not, although imaging provides information on mechanism. By this measure, in the group that received the most cells, the MACE rate was half that of controls. But comparing the placebo group versus the entire treatment group, there was not a significant effect on MACE.
Quyyumi says that additional follow-up should make the effect of cell therapy treatment on clinical outcomes even more clear: "It is encouraging to see clinically meaningful results this early in the study, and I look forward to future data readouts."
NeoStem executives have said that during the study, they were able to standardize their procedures so that in the future, every patient should be able to receive 20 million CD34+ cells. Quyyumi says the research team checked whether patients’ pre-existing levels of CD34+ cells in their bone marrow had a significant effect on their outcomes; they did not.
"If we assume CD34 positive cells are where the action is, it’s clear that you need big numbers," Quyyumi says. "This is a lesson for the cell therapy field moving forward."