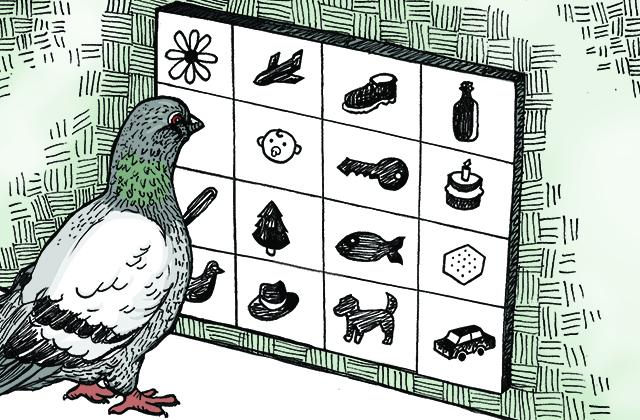
 Illustration by John Petsel (B.F.A. '15 in graphic design).The more scientists study pigeons, the more they learn how their brains—no bigger than the tip of an index finger—operate in ways not so different from our own.
Illustration by John Petsel (B.F.A. '15 in graphic design).The more scientists study pigeons, the more they learn how their brains—no bigger than the tip of an index finger—operate in ways not so different from our own.
In a new study from the University of Iowa, researchers found that pigeons can categorize and name both natural and manmade objects—and not just a few objects. These birds categorized 128 photographs into 16 categories, and they did so simultaneously.
Ed Wasserman, UI professor of psychology and corresponding author of the study, says the finding suggests a similarity between how pigeons learn the equivalent of words and the way children do.
“Unlike prior attempts to teach words to primates, dogs, and parrots, we used neither elaborate shaping methods nor social cues,” Wasserman says of the study, published online in the journal Cognition. “And our pigeons were trained on all 16 categories simultaneously, a much closer analog of how children learn words and categories.”
For researchers like Wasserman, who has been studying animal intelligence for decades, this latest experiment is further proof that animals—whether primates, birds, or dogs—are smarter than once presumed and have more to teach scientists.
“It is certainly no simple task to investigate animal cognition; But, as our methods have improved, so too have our understanding and appreciation of animal intelligence,” he says. “Differences between humans and animals must indeed exist: many are already known. But, they may be outnumbered by similarities. Our research on categorization in pigeons suggests that those similarities may even extend to how children learn words.”
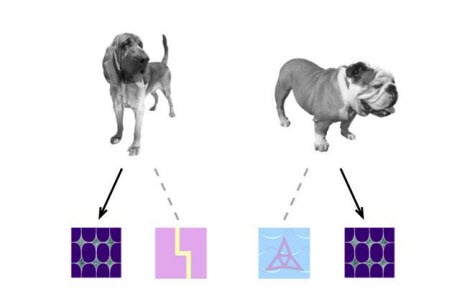 The pigeons learned to associate a specific icon for each of 16 basic categories which included "dog." The pigeons were shown a black-and-white photograph of a dog along with two icons—one that represented the word dog and the other that was randomly selected. If the pigeon pecked on the right icon, it was rewarded with pellets of food. Over time, the pigeons learned the icon for “dog” was a category that included photographs of a variety of dog breeds, like those shown above. They made the same association for 15 other categories.University of IowaWasserman says the pigeon experiment comes from a project published in 1988 and featured in The New York Times in which UI researchers discovered pigeons could distinguish among four categories of objects.
The pigeons learned to associate a specific icon for each of 16 basic categories which included "dog." The pigeons were shown a black-and-white photograph of a dog along with two icons—one that represented the word dog and the other that was randomly selected. If the pigeon pecked on the right icon, it was rewarded with pellets of food. Over time, the pigeons learned the icon for “dog” was a category that included photographs of a variety of dog breeds, like those shown above. They made the same association for 15 other categories.University of IowaWasserman says the pigeon experiment comes from a project published in 1988 and featured in The New York Times in which UI researchers discovered pigeons could distinguish among four categories of objects.
This time, the UI researchers used a computerized version of the “name game” in which three pigeons were shown 128 black-and-white photos of objects from 16 basic categories: baby, bottle, cake, car, cracker, dog, duck, fish, flower, hat, key, pen, phone, plan, shoe, tree. They then had to peck on one of two different symbols: the correct one for that photo and an incorrect one that was randomly chosen from one of the remaining 15 categories. The pigeons not only succeeded in learning the task, but they reliably transferred the learning to four new photos from each of the 16 categories.
Pigeons have long been known to be smarter than your average bird—or many other animals, for that matter. Among their many talents, pigeons have a “homing instinct” that helps them find their way home from hundreds of miles away, even when blindfolded. They have better eyesight than humans and have been trained by the U. S. Coast Guard to spot orange life jackets of people lost at sea. They carried messages for the U.S. Army during World Wars I and II, saving lives and providing vital strategic information.
UI researchers say their expanded experiment represents the first purely associative animal model that captures an essential ingredient of word learning—the many-to-many mapping between stimuli and responses.
“Ours is a computerized task that can be provided to any animal, it doesn’t have to be pigeons,” says UI psychologist Bob McMurray, another author of the study. “These methods can be used with any type of animal that can interact with a computer screen.”
McMurray says the research shows the mechanisms by which children learn words might not be unique to humans.
“Children are confronted with an immense task of learning thousands of words without a lot of background knowledge to go on,” he says. “For a long time, people thought that such learning is special to humans. What this research shows is that the mechanisms by which children solve this huge problem may be mechanisms that are shared with many species.”
Wasserman acknowledges the recent pigeon study is not a direct analogue of word learning in children and more work needs to be done. Nonetheless, the model used in the study could lead to a better understanding of the associative principles involved in children’s word learning.
“That’s the parallel that we’re pursuing,” he says, “but a single project—however innovative it may be—will not suffice to answer such a provocative question.”
National Institute of Mental Health Grant MH47313, National Eye Institute Grant EY019781, and National Institute of Deafness and Other Communication Disorders Grant DC0008089 supported the research.




 Illustration by John Petsel (B.F.A. '15 in graphic design).
Illustration by John Petsel (B.F.A. '15 in graphic design).








