Unstimulated synapse vs. stimulated synapse.Image Courtesy of Kausik Si LabKANSAS CITY, MO—During the holidays, we often remember the past and create new memories. But, why do some memories fade away while others last forever? Scientists at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research have identified a possible biochemical mechanism by which the specialized brain cells known as neurons create and maintain a long-term memory from a fleeting experience.
Unstimulated synapse vs. stimulated synapse.Image Courtesy of Kausik Si LabKANSAS CITY, MO—During the holidays, we often remember the past and create new memories. But, why do some memories fade away while others last forever? Scientists at the Stowers Institute for Medical Research have identified a possible biochemical mechanism by which the specialized brain cells known as neurons create and maintain a long-term memory from a fleeting experience.
The research, conducted by Stowers Associate Investigator Kausik Si, PhD, and his team, is published in the current issue of the journal Cell. Their research builds upon previous studies by Si and Eric Kandel, MD, of Columbia University and other scientists. These studies revealed that both short-term and long-term memories are created in synapses, the tiny junctions between neurons. A transient experience–one source of our memories–is capable of producing an enduring change in the strength of the synaptic connection, says Si.
Related article: Electrical Stimulation ‘Tunes’ Visual Attention Using Long-Term Memory
For a memory to endure, and not fade away, the synaptic connections must be kept strong. In a previous study, Kandel and Si identified CPEB as a synaptic protein that is responsible for maintaining the strength of these connections in the sea slug, a model organism used in memory research. In subsequent research at the Stowers Institute, Si and his team identified Orb2 as the fruit fly version of the CPEB synaptic protein.
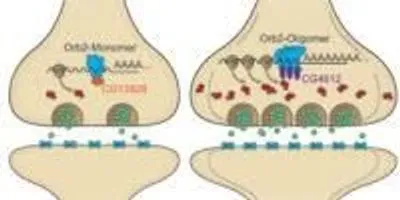
In their latest study, Mohammed 'Repon' Khan, a predoctoral researcher in the Si Lab and first author of the Cell paper, determined that Orb2 exists in two distinct physical states, monomeric and oligomeric. Monomeric Orb2 is a single molecule capable of binding to other molecules. Like CPEB, oligomeric Orb2 is prion-like–that is, it’s a self-copying cluster. However, unlike disease-causing prions, oligomeric Orb2 and CPEB are not toxic.
The paper describes how monomeric Orb2 represses while oligomeric or prion-like Orb2 activates a crucial step in the complex cellular process that leads to protein synthesis. During this crucial step, messenger RNA (mRNA), which is a RNA copy of a gene’s recipe for a protein, is translated by the cell’s ribosome into the sequence of amino acids that will make up a newly synthesized protein.
Related article: Scientists Explain How Memories Stick Together
“We propose that the monomeric form of Orb2 binds to the target mRNA, and the bound mRNA is kept in a repressed state,” explains Khan.
The Stowers scientists also determined that prion-like Orb2 not only activates translation but imparts its translational state to nearby monomer forms of Orb2. As a result, monomeric Orb2 is transformed into prion-like Orb2, and its role in translation switches from repression to activation. Si thinks this switch is the possible mechanism by which fleeting experiences create an enduring memory.
“Because of the self-sustaining nature of the prion-like state, this creates a local and self-sustaining translation activation of Orb2-target mRNA, which maintains the changed state of synaptic activity over time,” says Si.
The discovery that the two distinct states of Orb2 have opposing roles in the translation process provides “for the first time a biochemical mechanism of synapse-specific persistent translation and long-lasting memory,” he states.
Related article: Watching Molecules Morph into Memories
“To our knowledge, this is the first example of a prion-based protein switch that turns a repressor into an activator,” Si adds. “The recruitment of distinct protein complexes at the non-prion and prion-like forms to create altered activity states indicates the prion-like behavior is in essence a protein conformation-based switch. Through this switch, a protein can lose or gain a function that can be maintained over time in the absence of the original stimuli. Although such a possibility has been anticipated prior to this study, there was no direct evidence.”
Other Stowers contributors to this work include Liying Li, Consuelo Pérez-Sánchez, Anita Saraf, PhD, Laurence Florens, PhD, Brian Slaughter, PhD, and Jay Unruh, PhD.