Industry News

The southeastern United States is a natural laboratory for scientists studying how chemicals emitted by human activities and trees interact with each other and affect air quality and climate. A new study has found that certain emissions from cars and coal-fired power plants promote processes that transform naturally occurring emissions from trees into organic aerosols. Organic aerosols make up a substantial fraction of ambient particulate matter (PM) that can affect climate, air quality and human health.
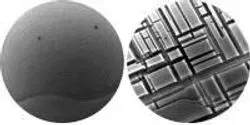
Rust never sleeps. Whether a reference to the 1979 Neil Young album or a product designed to protect metal surfaces, the phrase invokes the idea that corrosion from oxidation—the more general chemical name for rust and other reactions of metal with oxygen—is an inevitable, persistent process. But a new study performed at the Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN) at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory reveals that certain features of metal surfaces can stop the process of oxidation in its tracks.

Researchers at the University of California, Davis, will explore ways to speed production of the Ebola drug Zmapp with a $200,000 rapid-response grant from the National Science Foundation.

The world owes a debt of gratitude to Simon Fraser University (SFU) biologist Regine Gries. Her arms have provided a blood meal for more than a thousand bedbugs each week for five years while she and her husband, biology professor Gerhard Gries, searched for a way to conquer the global bedbug epidemic.

Scientists at the University of Cambridge working with the Weizmann Institute have created primordial germ cells – cells that will go on to become egg and sperm – using human embryonic stem cells. Although this had already been done using rodent stem cells, the study, published Dec. 24 in the journal Cell, is the first time this has been achieved efficiently using human stem cells.













