News

University of Adelaide scientists have identified the genes in wheat that control tolerance to a significant yield-limiting soil condition found around the globe - boron toxicity.

In chambers that mimic Mars' conditions, University of Michigan researchers have shown how small amounts of liquid water could form on the planet despite its below-freezing temperatures.
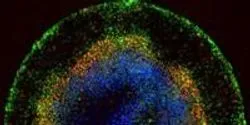
About seven days after conception, something remarkable occurs in the clump of cells that will eventually become a new human being. They start to specialize. They take on characteristics that begin to hint at their ultimate fate as part of the skin, brain, muscle or any of the roughly 200 cell types that exist in people, and they start to form distinct layers.

A new biosensor invented at the University of British Columbia could help optimize bio-refining processes that produce fuels, fine chemicals and advanced materials by sniffing out naturally occurring bacterial networks that are genetically wired to break down wood polymer.

Membrane developed by MIT researchers can separate even highly mixed fine oil-spill residues.

Bacteria are a pervasive and elusive bunch. Scientists estimate that between 10 million and 1 billion different microbial species populate the world, yet only a handful of them have so far been identified. Why? Because the overwhelming majority of microbes refuse to grow in the laboratory. This is despite decades of scientists’ best efforts at coaxing the microscopic organisms into action.

A forensics investigator dusts a crime scene for fingerprints. When she finds one, she reaches to her holster, pulls out a handheld device, and aims it at the fingerprint. The device captures the image and also the chemical composition. That chemical analysis reveals that the person who left the print had touched ephedrine—an illegal drug, which is a stimulant that goes by many street names, including meow. With this information, the investigators can use biometrics—the fingerprint— to identify the person and the chemical analysis to start piecing together the crime.

The University of Adelaide has been awarded more than $3.8 million by the Australian Research Council (ARC) to collaborate with industry on a range of projects spanning fields such as computer science, genetics, agriculture, engineering, communications, physics and the environment.

For the ever-shrinking transistor, there may be a new game in town. Cornell University researchers have demonstrated promising electronic performance from a semiconducting compound with properties that could prove a worthy companion to silicon











