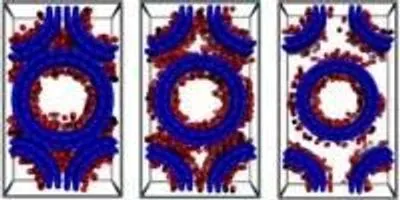
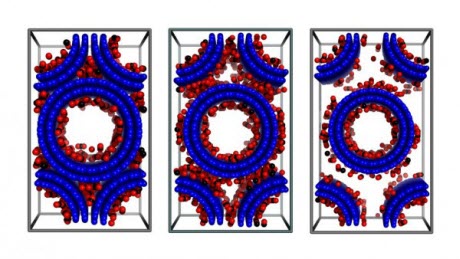
 Snapshots of CO2 adsorption in double-walled carbon nanotube arrays (with an inner tube diameter of 2r=3 nanometers and various inter-tube distance at T=303 K and p=1 bar).Image credit: Rahimi/BabuNewswise — WASHINGTON, D.C., September 22, 2015 -- Emissions from the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas tend to collect within Earth's atmosphere as "greenhouse gases" that are blamed for escalating global warming.
Snapshots of CO2 adsorption in double-walled carbon nanotube arrays (with an inner tube diameter of 2r=3 nanometers and various inter-tube distance at T=303 K and p=1 bar).Image credit: Rahimi/BabuNewswise — WASHINGTON, D.C., September 22, 2015 -- Emissions from the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas tend to collect within Earth's atmosphere as "greenhouse gases" that are blamed for escalating global warming.
So researchers around the globe are on a quest for materials capable of capturing and storing greenhouse gases. This shared goal led researchers at Technische Universität Darmstadt in Germany and the Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur to team up to explore the feasibility of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes (VACNTs) to trap and store two greenhouse gases in particular: carbon dioxide (CO2) and sulfur dioxide (SO2).
As the team reports in The Journal of Chemical Physics, from AIP Publishing, they discovered that gas adsorption in VACNTs can be influenced by adjusting the morphological parameters of the carbon nanotube thickness, the distance between nanotubes, and their height.
"These parameters are fundamental for 'tuning' the hierarchical pore structure of the VACNTs," explained Mahshid Rahimi and Deepu Babu, the paper's lead authors and doctoral students in theoretical physical chemistry and inorganic chemistry at the Technische Universität Darmstadt. "This hierarchy effect is a crucial factor for getting high-adsorption capacities as well as mass transport into the nanostructure. Surprisingly, from theory and by experiment, we found that the distance between nanotubes plays a much larger role in gas adsorption than the tube diameter does."
Typical carbon materials used in gas adsorption/desorption applications show huge hysteresis effects–in which the value of the physical property lags behind the changes in the effect causing it–due to pore size structure and distribution, so the team originally set out to "gain a deeper experimental and theoretical understanding of the fundamentals of adsorption and selectivity in carbon materials, as well as their application potential," they added.
The team chose VACNTs as a material to explore because they are created via a chemical vapor deposition process, which makes it possible to achieve a dense growth and regular tight packing of carbon nanotubes. VACNTs are "ideal model structures on which theory and experiment can be probed," said Rahimi and Babu.
Why is the dense growth and tight packing of carbon nanotubes important? "It allows our team to introduce well-defined adsorption sites that can be explored theoretically and creates an ideal symbiosis between experiment and theory," Rahimi said. "For theory, we rely on a molecular simulation method to simulate the adsorption process so it's as similar to the experiment as possible. This lets us predict what will happen in a much cheaper way, as well as explore what's happening in the experimentally studied system more deeply."
The team's most recent findings show that the gas adsorption provided by VACNTs is superior to typical adsorption materials such as porous carbon, zeolites and metal organic frameworks within the mid-pressure (30 bars) regime. "This adsorption range is important for technologically relevant processes like gas storage for automotive purposes," noted Rahimi.
As far as their future plans, the team will continue studying gas adsorption and selectivity under electrical charging conditions in VACNT structures. "Beyond this, we'll introduce specific atoms to achieve controlled elemental doping of the carbon nanotubes," she added. "This will allow us to further tune the gas selectivity. Another area we'll also explore is 'controlled carbon nanotube openings' in such VACNTs to increase the gas adsorption."
The article, "Double-walled carbon nanotube array for CO2 and SO2 adsorption," is authored by Mahshid Rahimi, Deepu J. Babu, Jayant K. Singh, Yong-Biao Yang, Jörg J. Schneider and Florian Müller-Plathe. It will appear in the Journal of Chemical Physics on September 22, 2015, (DOI: 10.1063/1.4929609). After that date, it can be accessed at: http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/jcp/143/12/10.1063/1.4929609
The authors of this study are affiliated with Technische Universität Darmstadt in Germany and the Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur in India.