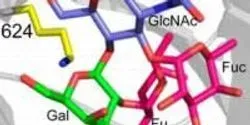
Biological Sciences


Brownfield sites—mainly abandoned or soon-to-be abandoned industrial facilities—pose huge challenges to governments, communities, and engineering firms charged with restoring them to common uses. At issue are contaminants—chemicals and metals—that if not remediated pose public health concerns.
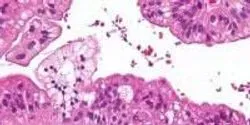
Researchers at the Virginia Bioinformatics Institute of Virginia Tech have discovered new possibilities for detecting ovarian cancer using microsatellite variations.

A family of proteins known as histones provides support and structure to DNA, but for years, scientists have been puzzling over occasional outliers among these histones, which appear to exist for specific, but often mysterious reasons. Now, researchers have uncovered a new purpose for one such histone variant: preventing genetic mutations by keeping certain so-called “jumping genes” in place.
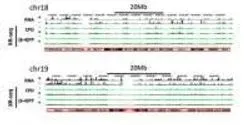
The new experimental assay can help scientists find the precise locations of repair of DNA damage caused by UV radiation and common chemotherapies. The invention could lead to better cancer drugs or improvements in the potency of existing ones.

The switchgrass exhibited mosaic symptoms—splotchy, discolored leaves—characteristic of a viral infection, yet tested negative for known infections. Deep sequencing, a new technology, revealed the plants were infected with a new virus in the genus mastrevirus, the first of its kind found in North America.