Biological Sciences

Alcohol consumption isn’t the only thing a breath analysis can reveal. Scientists have been studying its possible use for diagnosing a wide range of conditions in humans — and now in the beloved bottlenose dolphin. In a report in the American Chemical Society (ACS) journal Analytical Chemistry, one team describes a new instrument that can analyze the metabolites in breath from dolphins, which have been dying in alarming numbers along the Atlantic coast this year.

University of Haifa researchers find a functional link between the brain region responsible for taste memory and the area responsible for encoding the time and place we experienced the taste.

Lisa Taneyhill, Ph.D., an assistant professor in the Department of Animal and Avian Sciences at the University of Maryland, has been awarded a $1.9 million research grant from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research at the National Institutes of Health (NIH).

Fusion energy almost sounds too good to be true – zero greenhouse gas emissions, no long-lived radioactive waste, a nearly unlimited fuel supply.

Ebola, as with many emerging infections, is likely to have arisen due to man’s interaction with wild animals – most likely the practice of hunting and eating wild meat known as ‘bushmeat’. A team of researchers led by the University of Cambridge and the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) has surveyed almost six hundred people across southern Ghana to find out what drives consumption of bat bushmeat – and how people perceive the risks associated with the practice.

Problem: The assessment of cell concentration and viability is an important step in the characterization of cell health. This information can be used for monitoring proliferation rates, optimizing growth conditions and normalizing cell data for further studies, such as assessing the impacts of cytotoxic compounds.
Current methods rely on multiple, sometimes complex, instrument platforms to provide these answers, reducing flexibility and increasing research costs. Other, simpler methods provide inconsistent results due to their dependence on single-uptake dyes, which do not effectively discriminate between the various states of cell demise. As a result, there is a crucial need for analytical methods that efficiently provide reproducible count and viability data.
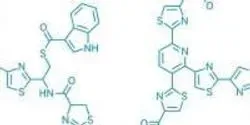
As the threat of antibiotic resistance grows, scientists are turning to the human body and the trillion or so bacteria that have colonized us — collectively called our microbiota — for new clues to fighting microbial infections. They've logged an early success with the discovery of a new antibiotic candidate from vaginal bacteria, reports Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society.