Physical Sciences

Twisted light from ancient stars may have played a role in locking in aspects of the structure of life on Earth, and new findings from the University of Michigan provide insights into how that process may have occurred.
Testing for ovarian cancer or the presence of a particular chemical could be almost as simple as distinguishing an F sharp from a B flat, thanks to a new microscopic acoustic device that has been dramatically improved by scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory.

A team of New York University and University of Barcelona physicists has developed a method to control the movements occurring within magnetic materials, which are used to store and carry information. The breakthrough could simultaneously bolster information processing while reducing the energy necessary to do so.

Since the 1850s scientists have known that crystalline materials are organized into 14 different basic lattice structures. However, a team of researchers from Vanderbilt University and Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) now reports that it has discovered an entirely new form of crystalline order that simultaneously exhibits both crystal and polycrystalline properties, which they describe as “interlaced crystals.”
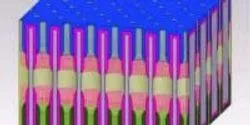
Researchers at the University of Maryland have invented a single tiny structure that includes all the components of a battery that they say could bring about the ultimate miniaturization of energy storage components.

The University of Delaware’s Mark Moline knew that his grandfather, O. Karl Olander, was a Navy chaplain in the Pacific during World War II. But it wasn’t until his mother shared his grandfather’s journal and scrapbook that Moline realized his grandfather had been on the USS Princeton, one of the aircraft carriers that attacked Palau in March 1944.

The seemingly simple process of phase changes—those transitions between states of matter—is more complex than previously known, according to research based at Princeton University, Peking University and New York University.















