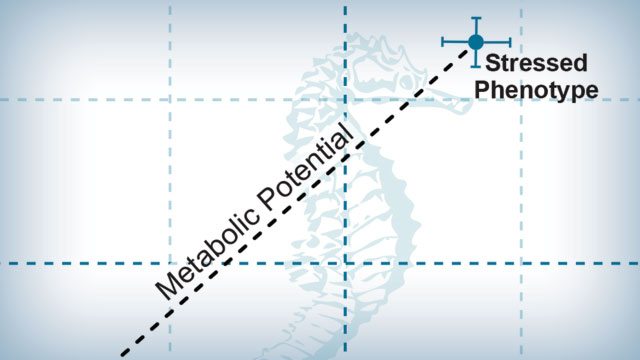
 Baseline Phenotype: Measurement of the cells’ relative utilization of mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis under starting conditions. Stressed Phenotype: Measurement of the cells' relative utilization of aerobic respiration and glycolysis under an energy demand. Metabolic Potential: Measurement of the cells' ability to meet an energy demand via mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis.
Baseline Phenotype: Measurement of the cells’ relative utilization of mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis under starting conditions. Stressed Phenotype: Measurement of the cells' relative utilization of aerobic respiration and glycolysis under an energy demand. Metabolic Potential: Measurement of the cells' ability to meet an energy demand via mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis.
Problem: Metabolism is at the core of cell biology, and metabolic dysfunction is known to play a major role in disease pathology and etiology. Mitochondria govern cell metabolism, generating energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) via the two major energy-producing pathways of the cell— mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis. The relative contribution of these two pathways enables cells to perform vital day-to-day functions and also contributes to the prevention of disease onset or progression. To date, gaining an understanding of cell metabolism, specifically mitochondrial respiration and glycolytic activity, has required running multiple, separate assays and then comparing the resulting data.
For example, gene and protein expression data can reveal metabolic dysregulation in a disease state. However, functional validation of these data has been limited to scientists who have the expertise in understanding the multiple assays and data analysis required to characterize the metabolic phenotype (the reflection of the relative utilization of both energy pathways). A lack of specialized expertise has prevented many other scientists from validating their functional metabolic data.
Solution: The XFp Cell Energy Phenotype Test, developed by Seahorse Bioscience, solves this problem by providing a single assay that measures the metabolic phenotype of a single cell or a group of live cells. Researchers can now quickly realize the functional consequences of somatic mutations or drug treatments in terms of metabolic adaptations and also better understand reprogramming events that drive disease.
This test, used with the XFp Analyzer, simultaneously measures the two energy pathways of a cell— mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis—enabling the full analysis of a metabolic phenotype without the additional work of standard curves, plate-to-plate comparison or multiple complimentary metabolic assays.
By simultaneously assessing mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis under both basal and stressed conditions, the XFp Cell Energy Phenotype Test rapidly determines the metabolic phenotype of cells, revealing their metabolic potential in one assay, and in less than one hour. This dramatically simplifies and standardizes how scientists can categorize the metabolic state and potential of a living cell under the most relevant in vitro conditions.
Insight into which preferred energy pathway (mitochondrial respiration or glycolysis) the cell utilizes helps scientists determine the next appropriate assay for further investigation. For example, if a reliance on mitochondrial respiration is observed, further analysis could be performed by running the XF Cell Mito Stress Test to more completely assess the parameters of mitochondrial function including basal respiration, maximal respiration and spare respiratory capacity.
In summary, because all cells use various combinations of mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis to generate ATP to satisfy biosynthetic demands, it is now recognized that cell metabolism research is best served by simultaneously measuring both energy-producing pathways and to interpret how they intertwine under normal and disease states. Understanding the balance between these two pathways presents a holistic view of cell energy production and utilization, enabling scientists to generate new insights into metabolic function, which can lead to greater comprehension and new treatments of disease.
For more information, please visit www.seahorsebio.com