Traditionally, metabolic assays employed a variety of instruments and techniques including Clark electrodes to measure oxygen consumption, “omic” platforms to detect increases and decreases in metabolic gene and protein expression, fluorescent and radiometric tags of various enzymes and substrates to estimate metabolic activity, and luminescent ATP assays as a surrogate of total energy metabolism. The value of these approaches is lessened by the fact that they are destructive, insensitive, indirect, single-point measurements, use invasive labels, and most importantly lack the functional context of a living cell.
Solution: The Seahorse Bioscience XFp Extracellular Flux Analyzer simultaneously measures mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis, the two major energy-producing pathways in a cell, in a cell culture microplate, in real time. XF technology works with a variety of cells offering physiologically relevant cellular bioenergetic assays, with comparable performance to biochemical and radioactive methods, with better throughput, and without the preparation and use of labels or radioactive materials. Thus, this technology overcomes many of the challenges and weaknesses of traditional endpoint assays that either directly or indirectly measure metabolic function.
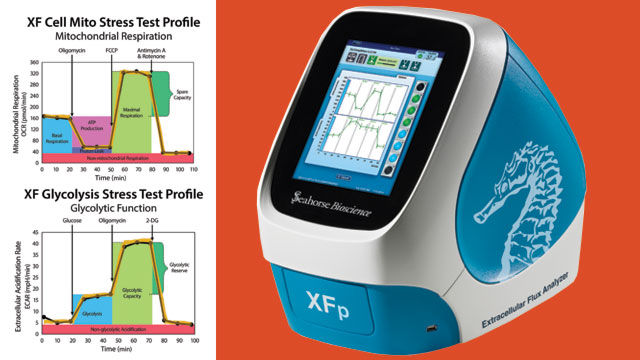
XF technology has led to the establishment of the Gold standard assays to measure metabolic function such as the Cell Mito Stress Test to measure mitochondrial function, the Glycolysis Stress Test to measure glycolytic function, the Metabolic Flexibility Assay, and the Metabolic Switching PhenoGram to illustrate metabolic switching.
The XFp Analyzer uses sensor arrays to measure extracellular fluxes in oxygen consumption (OCR) and extracellular acidification (ECAR), indicative of mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis, respectively. This technology allows measurements to be taken in minutes rather than hours, and prevents significant oxygen tension depression or media acidification.
Four injector ports surround each XFp Miniplate well and can be used for multiple injections of reagents to probe metabolic function, fuels and pathways in intact cells as well as generating dose-response curves. XF assays are labelfree and non-destructive, allowing the user to perform ATP or other viability assays on the same cell plate to generate additional information and/or normalize the XF data.
The role of cell metabolism in cellular and physiological processes is well established, with many diseases now linked to metabolic dysfunction. With XF technology, scientists can quickly and easily obtain functional metabolic data and gain a greater understanding of cell metabolism, enabling new advancements in life science research.
For more information, visit www.seahorsebio.com/xfp