Content by The Rockefeller University
Filter by
AllArticlesAudioEbooksEventsInfographicsNewsProductsSurveysDocumentsVideosVirtual EventsWebinars
A family of proteins known as histones provides support and structure to DNA, but for years, scientists have been puzzling over occasional outliers among these histones, which appear to exist for specific, but often mysterious reasons. Now, researchers have uncovered a new purpose for one such histone variant: preventing genetic mutations by keeping certain so-called “jumping genes” in place.

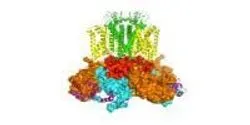
Bacteria may not have brains, but they do have memories, at least when it comes to viruses that attack them. Many bacteria have a molecular immune system which allows these microbes to capture and retain pieces of viral DNA that they have encountered in the past, in order to recognize and destroy it when it shows up again.

Forgetfulness, it turns out, is all in the head. Scientists have shown that fading memory and clouding judgment, the type that comes with advancing age, show up as lost and altered connections between neurons in the brain. But new experiments suggest an existing drug, known as riluzole and already on the market as a treatment for ALS, may help prevent these changes.

Stem cells in early embryos have unlimited potential; they can become any type of cell, and researchers hope to one day harness this rejuvenating power to heal disease and injury. To do so, they must, among other things, figure out how to reliably arrest stem cells in a Peter Pan-like state of indefinite youth and potential. It’s clear the right environment can help accomplish this, acting as a sort of Neverland for stem cells. Only now are scientists beginning to understand how.