The non-invasive neuroimaging technique used in this study could be employed to detect autism symptoms as early as infancyCREDIT: An et al., JNeurosci (2018)
The non-invasive neuroimaging technique used in this study could be employed to detect autism symptoms as early as infancyCREDIT: An et al., JNeurosci (2018)
A study of young children with autism spectrum disorder, published in JNeurosci, reveals altered brain waves compared to typically developing children during a motor control task. The non-invasive neuroimaging technique used in this study could be employed to detect autism symptoms as early as infancy.
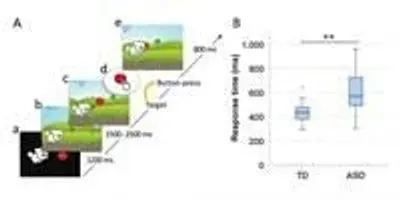
People with autism show reduced inhibitory neural activity, reflected in gamma brain waves, and movement abnormalities. Mitsuru Kikuchi and colleagues investigated these two aspects of the disorder by recording the brain activity of five- to seven-year-old children diagnosed with autism as they played a video game that required them to press a button to feed a puppy.
Compared to a matched group of typically developing children, the children with autism exhibited longer reaction times and reduced gamma oscillations that were associated with the severity of their symptoms. The researchers demonstrate that these features alone can distinguish the two groups, which may represent an objective approach toward diagnosing autism in young children.