 Michael Free (left) holds a light emitting diode and Prashant Sarswat (right) holds carbon dots in suspension.Photo credit: Prashant SarswatMost Christmas lights, televisions and flashlights have one thing in common: they’re made with light emitting diodes (LEDs). LEDs are widely used for a variety of applications and have been a popular, more efficient alternative to fluorescent and incandescent bulbs for the past few decades. Two University of Utah researchers have now found a way to create LEDs from food and beverage waste. In addition to utilizing food and beverage waste that would otherwise decompose and be of no use, this development can also reduce potentially harmful waste from LEDs generally made from toxic elements.
Michael Free (left) holds a light emitting diode and Prashant Sarswat (right) holds carbon dots in suspension.Photo credit: Prashant SarswatMost Christmas lights, televisions and flashlights have one thing in common: they’re made with light emitting diodes (LEDs). LEDs are widely used for a variety of applications and have been a popular, more efficient alternative to fluorescent and incandescent bulbs for the past few decades. Two University of Utah researchers have now found a way to create LEDs from food and beverage waste. In addition to utilizing food and beverage waste that would otherwise decompose and be of no use, this development can also reduce potentially harmful waste from LEDs generally made from toxic elements.
LEDs are a type of device that can efficiently convert electricity to light. Unlike fluorescent and incandescent bulbs, which direct 80% of the energy consumed to producing heat, LEDs direct 80% of the energy consumed to producing light. This is made possible by the fact that LEDs do not require a filament to be heated as incandescent and fluorescent bulbs do.
LEDs can be produced by using quantum dots, or tiny crystals that have luminescent properties, to produce light. Quantum dots (QDs) can be made with numerous materials, some of which are rare and expensive to synthesize, and even potentially harmful to dispose of. Some research over the past 10 years has focused on using carbon dots (CDs), or simply QDs made of carbon, to create LEDs instead.
Compared to other types of quantum dots, CDs have lower toxicity and better biocompatibility, meaning they can be used in a broader variety of applications.
U Metallurgical Engineering Research Assistant Professor Prashant Sarswat and Professor Michael Free, over the past year and a half, have successfully turned food waste such as discarded pieces of tortilla into CDs, and subsequently, LEDs.
The results were recently published in Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, a journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry.
From bread to bulb
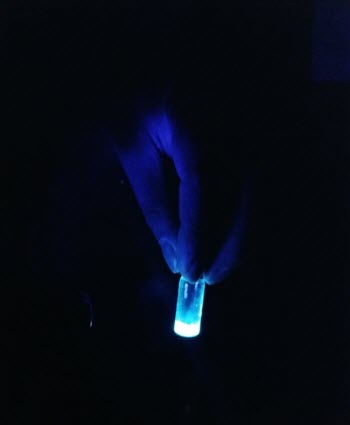 The luminescence of carbon dots can be seen when irradiated with UV light.Photo credit: Prashant SarswatTo synthesize waste into CDs, Sarswat and Free employed a solvothermal synthesis, or one in which the waste was placed into a solvent under pressure and high temperature until CDs were formed. In this experiment, the researchers used soft drinks and pieces of bread and tortilla.
The luminescence of carbon dots can be seen when irradiated with UV light.Photo credit: Prashant SarswatTo synthesize waste into CDs, Sarswat and Free employed a solvothermal synthesis, or one in which the waste was placed into a solvent under pressure and high temperature until CDs were formed. In this experiment, the researchers used soft drinks and pieces of bread and tortilla.
The food and beverage waste were each placed in a solvent and heated both directly and indirectly for anywhere from 30 to 90 minutes.
After successfully finding traces of CDs from the synthesis, Sarswat and Free proceeded to illuminate the CDs to monitor their formation and color.
The pair also employed four other tests, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Raman and AFM imaging to determine the CDs’ various optical and material properties.
“Synthesizing and characterizing CDs derived from waste is a very challenging task. We essentially have to determine the size of dots which are only 20 nanometers or smaller in diameter, so we have to run multiple tests to be sure CDs are present and to determine what optical properties they possess,” said Sarswat.
For comparison, a human hair is around 75,000 nanometers in diameter.
The various tests Sarswat and Free ran first measured the size of the CDs, which correlates with the intensity of the dots’ color and brightness. The tests then determined which carbon source produced the best CDs. For example, sucrose and D-fructose dissolved in soft drinks were found to be the most effective sources for production of CDs.
Finally, the CDs were suspended in epoxy resins, heated and hardened to solidify the CDs for practical use in LEDs.
An environmentally sustainable alternative
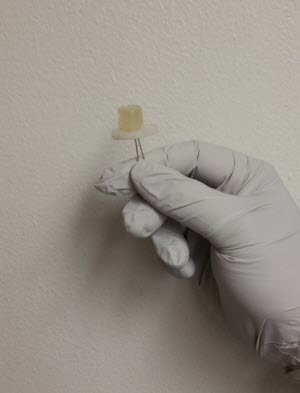 A small light emitting diode fabricated from carbon dots.Photo credit: Prashant SarswatCurrently, one of the most common sources of QDs is cadmium selenide, a compound comprised of a two toxic elements. The ability to create QDs in the form of CDs from food and beverage waste would eliminate the need for concern over toxic waste, as the food and beverages themselves are not toxic.
A small light emitting diode fabricated from carbon dots.Photo credit: Prashant SarswatCurrently, one of the most common sources of QDs is cadmium selenide, a compound comprised of a two toxic elements. The ability to create QDs in the form of CDs from food and beverage waste would eliminate the need for concern over toxic waste, as the food and beverages themselves are not toxic.
“QDs derived from food and beverage waste are not based on common toxic elements such as cadmium and selenium, which makes their processing and disposal more environmentally friendly than it is for most other QDs. In addition, the use of food and beverage waste as the starting material for QDs allows for reduced waste and cost to produce a useful material,” said Free.
In addition to being toxic when broken down, cadmium selenide is also expensive—one website listed a price of $529 for 25 ml of the compound.
“With food and beverage waste that are already there, our starting material is much less expensive. In fact, it’s essentially free,” said Sarswat.
According to a report from the US Department of Agriculture, roughly 31% of food produced in 2014 was not available for human consumption. To be able to use this waste for creating LEDs which are widely used in a number of technologies would be an environmentally sustainable approach.
Looking forward, Sarswat and Free hope to continue studying the LEDs produced from food and beverage waste for stability and long term performance.
“The ultimate goal is to do this on a mass scale and to use these LEDs in everyday devices. To successfully make use of waste that already exists, that’s the end goal,” said Sarswat.




 Michael Free (left) holds a light emitting diode and Prashant Sarswat (right) holds carbon dots in suspension.
Michael Free (left) holds a light emitting diode and Prashant Sarswat (right) holds carbon dots in suspension.









