Clinical Research Labs
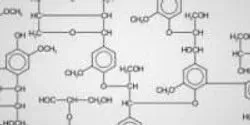
Researchers with the University of Florida’s Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences took what some would consider garbage and made a remarkable scientific tool, one that could someday help to correct genetic disorders or treat cancer without chemotherapy’s nasty side effects.

Diagnostic effectiveness is driving the accelerated acceptance of Stanbio Laboratory’s Beta Hydroxybutyrate LiquiColor® reagent in U.S. hospital chemistry laboratories. The assay is used primarily for determining both the presence and degree of ketosis in suspected diabetic ketoacidosis cases.

Researchers at the Wayne State University School of Medicine are among more than 250 scientists in 114 labs in more than 20 countries and regions to publish a series of coordinated papers, including landmark papers in Nature and ten other journals, revealing a definitive list of human cell states that has the potential to serve as an essential resource for regenerative medicine.

Killian Award recipient Stephen Lippard describes his work on platinum-based chemotherapy agents

Researchers at the Institute for Genome Sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine have been awarded a research program contract from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to sequence, assemble, and annotate a population of bacterial pathogens using two high-throughput sequencing (HTS) technologies in support of the expansion of a vetted public reference database.

A team of researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) has developed the world’s first fluorescent sensor to identify the presence of a drug known as GHB that is commonly used to spike beverages. When the sensor is mixed with a sample of a beverage containing GHB, the mixture changes colour in less than 30 seconds, making detection of the drug fast and easy.
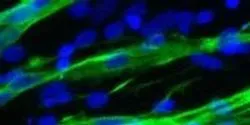
As stem cells continue their gradual transition from the lab to the clinic, a research group at the University of Wisconsin-Madison has discovered a new way to make large concentrations of skeletal muscle cells and muscle progenitors from human stem cells.

A University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center study has identified a new potential therapeutic target for controlling high blood sugar, a finding that could help the estimated 25 million Americans with type 2 diabetes.











