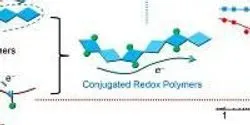
Polymers
The probe of an atomic force microscope (AFM) scans a surface to reveal details at a resolution 1,000 times greater than that of an optical microscope. That makes AFM the premier tool for analyzing physical features, but it cannot tell scientists anything about chemistry. For that they turn to the mass spectrometer (MS).

Using the same baking soda found in most grocery stores, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory scientists, along with colleagues from Harvard University and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, have created a significant advance in carbon dioxide capture.
New family of materials produces "twin" electrical charges on single molecules, potentially paving the way for easy manufacture of more efficient solar devices.

Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have used advanced microscopy to carve out nanoscale designs on the surface of a new class of ionic polymer materials for the first time. The study provides new evidence that atomic force microscopy, or AFM, could be used to precisely fabricate materials needed for increasingly smaller devices.