Analytical Instruments

Scientists’ underwater cameras got a boost this summer from the Electron Microscopy Center at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory. Along with colleagues at the University of Manchester, researchers captured the world’s first real-time images and simultaneous chemical analysis of nanostructures while “underwater,” or in solution.

Rigaku Raman Technologies, a leading pioneer of handheld and portable Raman spectrometers, will be showcasing its new generation handheld Raman analyzer for raw material identification (RMID) in booth 1C82 at CPhI Worldwide 2014 (7-9th October 2014. Paris Nord Villepinte, France). Progeny™ (http://www.rigakuprogeny.com) delivers improved performance, ease of use and confidence to ensure the industry’s most accurate and comprehensive range of material identification in a handheld form.
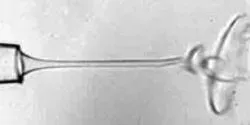
Industrial wet spinning processes produce fibers from polymers and other materials by using tiny needles to eject continuous jets of liquid precursors. The electrically charged liquids ejected from the needles normally exhibit a chaotic “whipping” structure as they enter a secondary liquid that surrounds the microscopic jets.

It may look like fresh blood and flow like fresh blood, but the longer blood is stored, the less it can carry oxygen into the tiny microcapillaries of the body, says a new study from University of Illinois researchers.

Research from University of Leicester sniffs-out smell of disease in feces.

Rigaku's Handheld Raman Analyzer Wins IBO Award for Portable Analytical Instrument Industrial Design
Rigaku Raman Technologies, a leading pioneer of handheld and portable Raman spectrometers, is delighted to announce that its handheld Raman analyzer, Progeny™ (www.rigakuprogeny.com) has received the Bronze Award for the Portable Analytical Instrument Industrial Design category in the 2014 Instrument Business Outlook (IBO) Design Awards.














