Microscopy

Pity the poor lithium ion. Drawn relentlessly by its electrical charge, it surges from anode to cathode and back again, shouldering its way through an elaborate molecular obstacle course. This journey is essential to powering everything from cell phones to cordless power tools. Yet, no one really understands what goes on at the atomic scale as lithium ion batteries are used and recharged, over and over again.

Scientists’ underwater cameras got a boost this summer from the Electron Microscopy Center at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory. Along with colleagues at the University of Manchester, researchers captured the world’s first real-time images and simultaneous chemical analysis of nanostructures while “underwater,” or in solution.
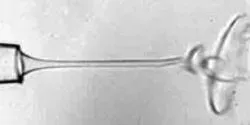
Industrial wet spinning processes produce fibers from polymers and other materials by using tiny needles to eject continuous jets of liquid precursors. The electrically charged liquids ejected from the needles normally exhibit a chaotic “whipping” structure as they enter a secondary liquid that surrounds the microscopic jets.

It may look like fresh blood and flow like fresh blood, but the longer blood is stored, the less it can carry oxygen into the tiny microcapillaries of the body, says a new study from University of Illinois researchers.