Biology

An international team of researchers has sequenced the nearly complete genome of two Siberian woolly mammoths—revealing the most complete picture to date—including new information about the species’ evolutionary history and the conditions that led to its mass extinction at the end of the Ice Age.

Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have been awarded two grants to study brain mechanisms that actively suppress relapse associated with cocaine and alcohol addiction.

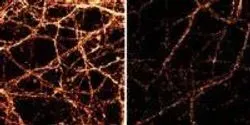
UT Southwestern Medical Center’s Texas Institute for Brain Injury and Repair (TIBIR) has acquired a pair of TissueCyte 1000 microscopes, the latest generation in serial two-photon laser imaging, as a centerpiece of its new Whole Brain Microscopy Facility. The TissueCyte microscopes are the only ones of their kind in Texas, and two of just a handful in existence around the world.

Scientists at the University of Manchester have discovered a way to make trees grow bigger and faster, which could increase supplies of renewable resources and help trees cope with the effects of climate change.

Johns Hopkins environmental scientists are collaborating with researchers from Dolphin Island at Resorts World Sentosa, Singapore, to learn more about how and where mercury accumulates in the bodies of Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphins.