Biology
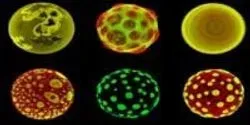
How did life originate? And can scientists create life? These questions not only occupy the minds of scientists interested in the origin of life, but also researchers working with technology of the future. If we can create artificial living systems, we may not only understand the origin of life - we can also revolutionize the future of technology.

Alcohol consumption isn’t the only thing a breath analysis can reveal. Scientists have been studying its possible use for diagnosing a wide range of conditions in humans — and now in the beloved bottlenose dolphin. In a report in the American Chemical Society (ACS) journal Analytical Chemistry, one team describes a new instrument that can analyze the metabolites in breath from dolphins, which have been dying in alarming numbers along the Atlantic coast this year.

Lisa Taneyhill, Ph.D., an assistant professor in the Department of Animal and Avian Sciences at the University of Maryland, has been awarded a $1.9 million research grant from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research at the National Institutes of Health (NIH).

Ebola, as with many emerging infections, is likely to have arisen due to man’s interaction with wild animals – most likely the practice of hunting and eating wild meat known as ‘bushmeat’. A team of researchers led by the University of Cambridge and the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) has surveyed almost six hundred people across southern Ghana to find out what drives consumption of bat bushmeat – and how people perceive the risks associated with the practice.

Americans love their dogs, but they don’t always love to pick up after them. And that’s a problem. Dog feces left on the ground wash into waterways, sometimes carrying bacteria — including antibiotic-resistant strains — that can make people sick. Now scientists have developed a new genetic test to figure out how much dogs are contributing to this health concern, according to a report in the American Chemical Society journal Environmental Science & Technology.
















