hydrogen
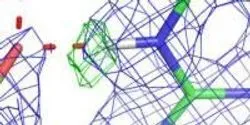
Enzymes are catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms and control many cellular biological processes by converting a molecule, or substrate, into a product used by the cell. For scientists, understanding details of how enzymes work is essential to the discovery of drugs to cure diseases and treat disorders.

Large-scale storage of low-pressure, gaseous hydrogen in salt caverns and other underground sites for transportation fuel and grid-scale energy applications offers several advantages over above-ground storage, says a recent Sandia National Laboratories study sponsored by the Department of Energy’s Fuel Cell Technologies Office.

Researchers at the US Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have created a small scale “hydrogen generator” that uses light and a two-dimensional graphene platform to boost production of the hard-to-make element.