Mass Spectrometers

Douglas Kiehl is a principal research scientist at Eli Lilly & Company, and is currently leader for the Spectroscopy & Raw Materials team. His group performs characterization and structural elucidation of impurities, related substances, and contaminants as well as testing and qualification of process raw materials through development and commercialization. Additionally, his team leads Lilly’s technical strategy for evaluating extractables and leachables associated with pharmaceutically relevant materials.

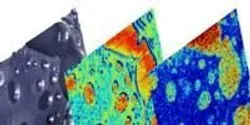
The probe of an atomic force microscope (AFM) scans a surface to reveal details at a resolution 1,000 times greater than that of an optical microscope. That makes AFM the premier tool for analyzing physical features, but it cannot tell scientists anything about chemistry. For that they turn to the mass spectrometer (MS).
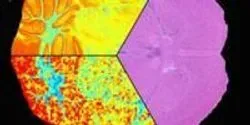
Vanderbilt University researchers have achieved the first “image fusion” of mass spectrometry and microscopy — a technical tour de force that could, among other things, dramatically improve the diagnosis and treatment of cancer.

Problem: In the analytical sciences the common image of mass spectrometry involves researchers in a core facility, analyzing spectra generated by a machine the size of a refrigerator. Because conventional mass spectrometers operate under extreme vacuum, they must be coupled with pumps that are expensive, bulky, noisy, and fragile. These powerhouse systems are designed to accommodate a wide variety of often-disparate needs, and this flexibility adds complexity in both operation and maintenance.















