DNA

Medical and other researchers and science teachers around the world will be able to compare ancient DNA from humans from thousands of years ago with the genetics of modern day humans, thanks to a new world-first open access databank at the University of Adelaide’s Australian Centre for Ancient DNA (ACAD).

Palaeontologist Dr Gareth Dyke writes for The Conversation about the scientific debate around the new Jurassic World film

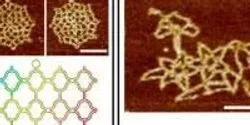
Scientists around the world are using the programmability of DNA to assemble complex nanometer-scale structures. Until now, however, production of these artificial structures has been limited to water-based environments, because DNA naturally functions inside the watery environment of living cells.

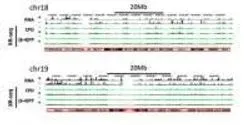
McGill University researchers devise new technique to produce long, custom-designed DNA strands.
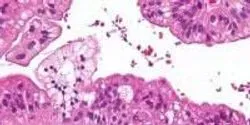
Researchers at the Virginia Bioinformatics Institute of Virginia Tech have discovered new possibilities for detecting ovarian cancer using microsatellite variations.