Cancer Treatments

A new study at the University of Wisconsin-Madison has linked two seemingly unrelated cancer treatments that are both now being tested in clinical trials.
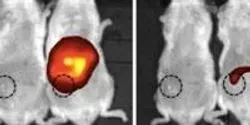
Researchers funded by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering have designed a nanoparticle transport system for gene delivery that destroys deadly brain gliomas in a rat model, significantly extending the lives of the treated animals. The nanoparticles are filled with genes for an enzyme that converts a prodrug called ganciclovir into a potent destroyer of the glioma cells.

For decades, scientists have known that ET-743, a compound extracted from a marine invertebrate called a mangrove tunicate, can kill cancer cells. The drug has been approved for use in patients in Europe and is in clinical trials in the U.S.

For decades, saccharin was wrongly labeled as a possible cancer-causing chemical. Now, nearly 15 years after it was declared safe, University of Florida Health researchers have found that the artificial sweetener can inhibit cancer cell growth.

Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have been awarded a $1.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to develop drug candidates that could treat cancer and neurodegenerative disease.

Movies like "Happy Feet" and "March of the Penguins" often remind us of how cute penguins are in the cold, Antarctic conditions where they live. These movies, however, fail to mention another species of penguin that reside in warmer climates and is slowly dying out: African penguins. Although they are on track to be extinct within the next 20 years, the Pueblo Zoo in Colorado and Colorado State University, Fort Collins recently performed cancer treatments on the oldest living African penguin in the world, ensuring that the penguin will be healthy enough to live a longer life.