FTIR / NIR

A newly developed spectroscopy method is helping to clarify the poorly understood molecular process by which an anti-HIV drug induces lethal mutations in the virus’ genetic material. The findings from the University of Chicago and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology could bolster efforts to develop the next generation of anti-viral treatments.
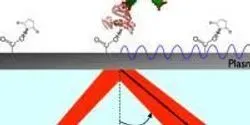
A research team led by North Carolina State University has identified and synthesized a material that can be used to create efficient plasmonic devices that respond to light in the mid-infrared (IR) range. This is the first time anyone has demonstrated a material that performs efficiently in response to this light range, and it has applications in fields ranging from high-speed computers, to solar energy to biomedical devices.

Any science textbook will tell you we can’t see infrared light. Like X-rays and radio waves, infrared light waves are outside the visual spectrum.

Rigaku Raman Technologies, a leading pioneer of handheld and portable Raman spectrometers, will be showcasing its new generation handheld Raman analyzer for raw material identification (RMID) in booth 1C82 at CPhI Worldwide 2014 (7-9th October 2014. Paris Nord Villepinte, France). Progeny™ (http://www.rigakuprogeny.com) delivers improved performance, ease of use and confidence to ensure the industry’s most accurate and comprehensive range of material identification in a handheld form.

Rigaku's Handheld Raman Analyzer Wins IBO Award for Portable Analytical Instrument Industrial Design
Rigaku Raman Technologies, a leading pioneer of handheld and portable Raman spectrometers, is delighted to announce that its handheld Raman analyzer, Progeny™ (www.rigakuprogeny.com) has received the Bronze Award for the Portable Analytical Instrument Industrial Design category in the 2014 Instrument Business Outlook (IBO) Design Awards.














