Materials Science
Testing for ovarian cancer or the presence of a particular chemical could be almost as simple as distinguishing an F sharp from a B flat, thanks to a new microscopic acoustic device that has been dramatically improved by scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory.

A team of New York University and University of Barcelona physicists has developed a method to control the movements occurring within magnetic materials, which are used to store and carry information. The breakthrough could simultaneously bolster information processing while reducing the energy necessary to do so.

Since the 1850s scientists have known that crystalline materials are organized into 14 different basic lattice structures. However, a team of researchers from Vanderbilt University and Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) now reports that it has discovered an entirely new form of crystalline order that simultaneously exhibits both crystal and polycrystalline properties, which they describe as “interlaced crystals.”
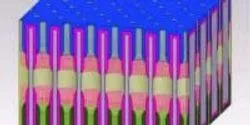
Researchers at the University of Maryland have invented a single tiny structure that includes all the components of a battery that they say could bring about the ultimate miniaturization of energy storage components.

Nanobodies' promise hasn’t been fully realized, because scientists have lacked an efficient way of identifying the nanobodies most closely tuned to their targets

Researchers from Columbia Engineering and the Georgia Institute of Technology have reported the first experimental observation of piezoelectricity and the piezotronic effect in an atomically thin material, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), resulting in a unique electric generator and mechanosensation devices that are optically transparent, extremely light, and very bendable and stretchable.















