DNA repair

Sites where DNA is damaged may cause a molecule that slides along the DNA strand to scan for damage to slow on its patrol, delaying it long enough to recognize and initiate repair. The finding suggests that the delay itself may be the key that allows the protein molecule to find its target, according to researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago.

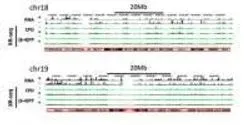
Ribonucleotides, units of RNA, can become embedded in genomic DNA during processes such as DNA replication and repair, affecting the stability of the genome by contributing to DNA fragility and mutability. Scientists have known about the presence of ribonucleotides in DNA, but until now had not been able to determine exactly what they are and where they are located in the DNA sequences.
The ability to accurately repair DNA damaged by spontaneous errors, oxidation or mutagens is crucial to the survival of cells. This repair is normally accomplished by using an identical or homologous intact sequence of DNA, but scientists have now shown that RNA produced within cells of a common budding yeast can serve as a template for repairing the most devastating DNA damage – a break in both strands of a DNA helix.