News

Human cells make new copies of their DNA billions of times each day, a crucial process upon which life itself depends. However, scientists do not fully understand how cells unzip the double-stranded DNA molecule before replicating both halves of it. New work at Rockefeller may help change that.
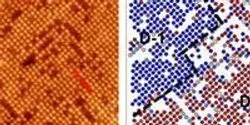
A novel combination of microscopy and data processing has given researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory an unprecedented look at the surface of a material known for its unusual physical and electrochemical properties.
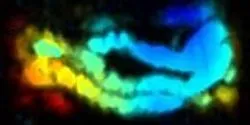
A multi-institutional team of researchers has developed a new nanoscale agent for imaging the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. This safe, noninvasive method for assessing the function and properties of the GI tract in real time could lead to better diagnosis and treatment of gut diseases.

Malvern Instruments Ltd (Malvern, UK) has today (July 25) announced that it has completed the acquisition of MicroCal from GE Healthcare Life Sciences and has also purchased the Archimedes particle characterization system from Affinity Biosensors LLC (Santa Barbara, CA). Both of these developments extend Malvern’s portfolio of analytical solutions for the rapidly advancing biopharmaceutical industry.

Blueberries pack a powerful antioxidant punch, whether eaten fresh or from the freezer, according to South Dakota State University graduate Marin Plumb.















