News

Nanomaterials commonly used in sunscreens and boat-bottom paints are making sea urchin embryos more vulnerable to toxins, according to a study from the University of California, Davis. The authors said this could pose a risk to coastal, marine and freshwater environments.

A new study analyzes the required climate policy actions and targets in order to limit future global temperature rise to less than 1.5°C by 2100. This level is supported by more than 100 countries worldwide, including those most vulnerable to climate change, as a safer goal than the currently agreed international aim of 2°C.

Agricultural officials who seek to detect diseases affecting the commercial swine industry may gain a new ally — a biological detection system developed by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers.

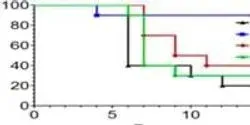
Grass plants can bind, uptake and transport infectious prions, according to researchers at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth). The research was published online in the latest issue of Cell Reports.