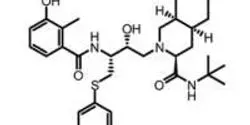
News

According to the public databases, there are currently approximately 1,900 locations in the human genome that produce microRNAs (miRNAs), the small and powerful non-coding molecules that regulate numerous cellular processes by reducing the abundance of their targets. New research published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) this week adds another roughly 3,400 such locations to that list. Many of the miRNA molecules that are produced from these newly discovered locations are tissue-specific and also human-specific. The finding has big implications for research into how miRNAs drive disease.

Bacteria may not have brains, but they do have memories, at least when it comes to viruses that attack them. Many bacteria have a molecular immune system which allows these microbes to capture and retain pieces of viral DNA that they have encountered in the past, in order to recognize and destroy it when it shows up again.

A Missouri University of Science and Technology professor has shown that improving wastewater treatment and saving energy are not only essential, but they’re also compatible.

The first nationwide vulnerability assessment for ocean acidification, published today in Nature Climate Change, shows that coastal communities in 15 states that depend on the nation’s approximately $1 billion shelled-mollusk (e.g., oysters and clams) industry are at long-term economic risk from ocean acidification.