Analytical Instruments
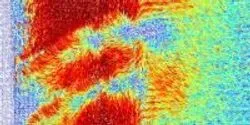
Device allows fast, precise measurements of electric and magnetic fields at the atomic level, providing insights into the next generation of electronic, energy production, and storage materials
| 3 min read

New $17 Million Cryo-Electron Microscope Center Provides Extraordinary Views of Life at Atomic Scale
Facility will help accelerate biomedical investigations on everything from cancer biology to drug discovery
| 4 min read



















